Enterprise Risk Management
Enterprise Risk Management
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is a plan-based business strategy that aims to identify, assess, and prepare for any uncertainties that could negatively or positively influence the achievement of the corporation’s objectives.
In the past, managing risk was done in a fragmented manner within functions or business units. Individuals would manage process risk; safety risk; and insurance, financial, and other assorted risks. As a result of this fragmented approach, companies would take huge risks in some areas of the business while overmanaging substantially smaller risks in other areas. ERM is being adopted because of the increasing amount of environmental uncertainty that can affect an entire corporation.
The discipline not only calls for corporations to identify all the risks they face and to decide which risks to manage actively, but it also involves making that plan of action available to all stakeholders, shareholders and potential investors, as part of their annual reports. The process of rating risks involves three steps:
- Identify the risks using scenario analysis, brainstorming, or by performing risk self-assessments.
- Rank the risks, using some scale of impact and likelihood.
- Measure the risks, using some agreed-upon standard.
In creating ERM initiatives, companies should focus not only on the downside of risk but on the upside as well.
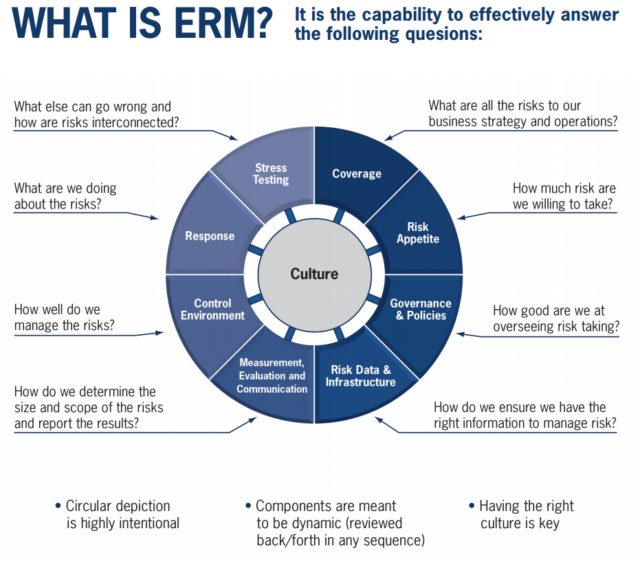
Pic 1. Enterprise Risk Management Framework (Source: https://www.rmahq.org/erm-framework/)
Below are descriptions of key components in a strong enterprise risk management plan:
- Business strategy and risk coverage
The institution must define what it wants to achieve in terms of markets, geographies, segments, products, earnings, and so on. From there, the institution assesses the risk implied in that strategy and determines the level of risk it is willing to assume in executing that strategy.
- Risk appetite
Risk appetite represents the acceptance of volatility an institution is willing to assume in executing its business strategy. It is important for management and the board of directors to understand the critical links among strategy, business plans, and risk. A risk appetite statement is one tool that facilitates this linkage.
- Culture, governance, and policies
Culture, governance, and policies collectively help an institution manage its risk-taking activities.
- Risk data and infrastructure
The risk data and infrastructure refer to how the information is collected, integrated, analyzed, and translated into a cohesive story.
- Control environment
Internal controls help reduce the level of inherent risk to a level acceptable to management. The system of internal controls includes culture, governance, policies, preventive and detective controls, and scenario planning. Building an effective internal control environment allows management to control what can be controlled.
- Measurement and evaluation
The process of measurement and evaluation must include the system of internal controls and must determine how well the risks can be managed.
- Scenario planning and stress testing
Scenario planning and stress testing are tools that focus on the knowable and, perhaps, some unknowable risks.
Enterprise Risk Management, essential for any institution, encompasses all relevant risks. An ERM framework and model supports a management competency to manage risks well, comprehensively, and with an understanding of the interrelationship/correlation among various risks. The successful institution incorporates a robust ERM capability and strategy as part of its culture by integrating what already exists to create a comprehensive and integrated view of the institution’s risk profile in the context of its business strategy.
Source:
Strategic Management and Business Policy: Globalization, Innovation, and Sustainability, 15th Edition, ISBN 978-0-13-452205-0 by Thomas L. Wheelen, David Hunger, Alan N. Hoffman, and Charles E. Bamford, published by Pearson Education © 2018.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/enterprise-risk-management.asp
https://www.rmahq.org/erm-framework/



Comments :